Melinda: This is how it looks when I turned on the microscope. I didn’t know how to make it focus on an object so I decided to find a manual on the internet to learn how to use the microscope properly.
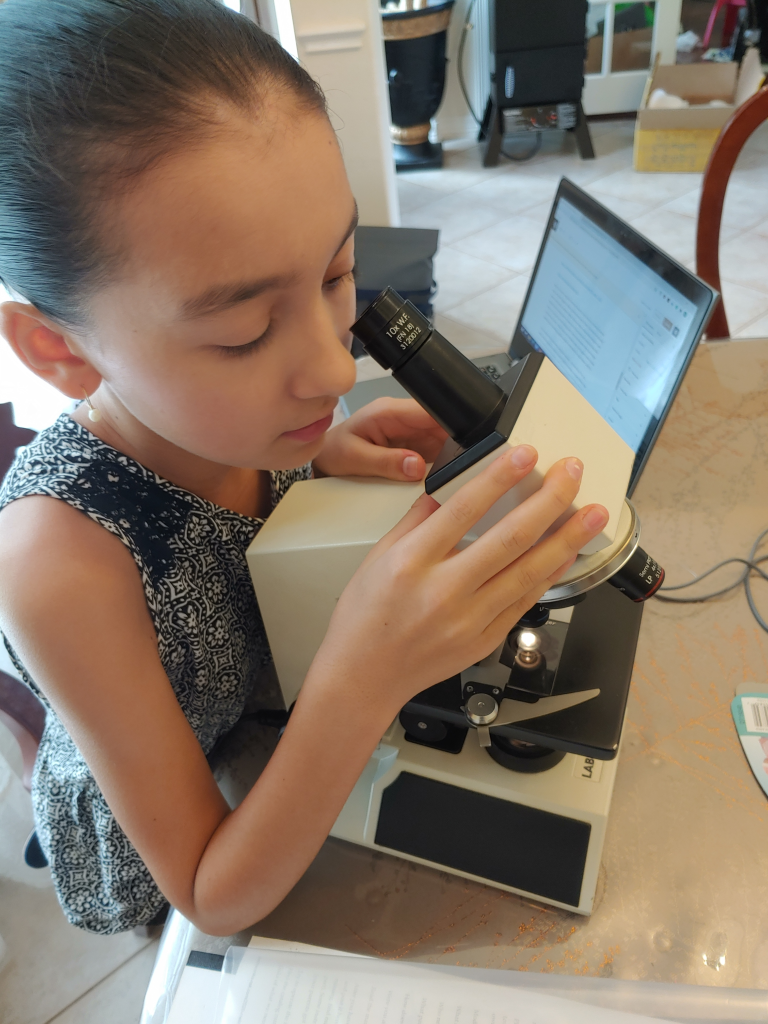
Melinda: Me looking through the microscope

So far I got to get the microscope to focus by following the directions of the manual. The manual really helped me figure out how to use the microscope properly by following all the directions given me step by step. Down below are the pictures I got by taking a picture from the phone. So far so good!
Melinda: I plan to move forward by every day studying different samples that I have and to also compare them from other samples by writing notes. Also, I really don’t know yet how to figure out what each part of the cell is called but I will figure that out.
Me studying a sample
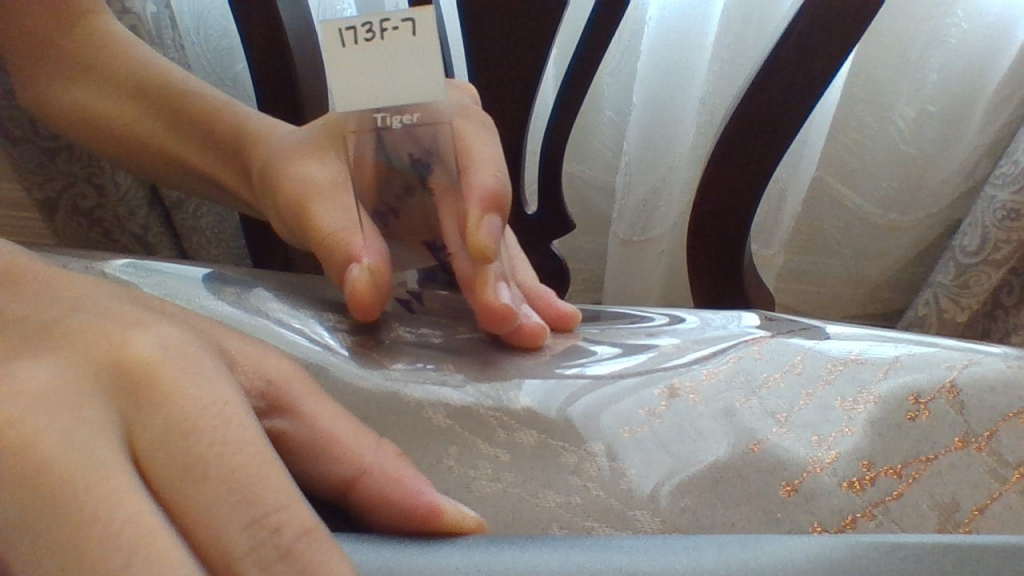

Melinda: This is the sample that I am studying right now.
I have also noticed that the difference between animal cells and plant cells:
Animal cells:
Smaller
- Have no cell wall
- Have a nucleus in the center
- Have many vacuoles
- Cannot synthesis nutrients
- No plasmodesmata
Plant Cells:
Larger
- Has a cell wall
- Nucleus on the side
- One Vacuole
- Synthesizes Nutrients
- Has Plasmodesmata
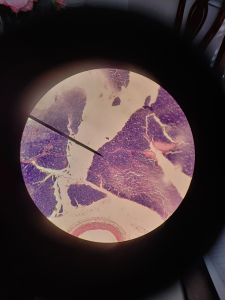
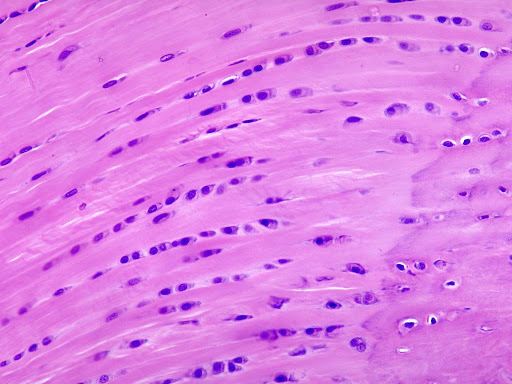
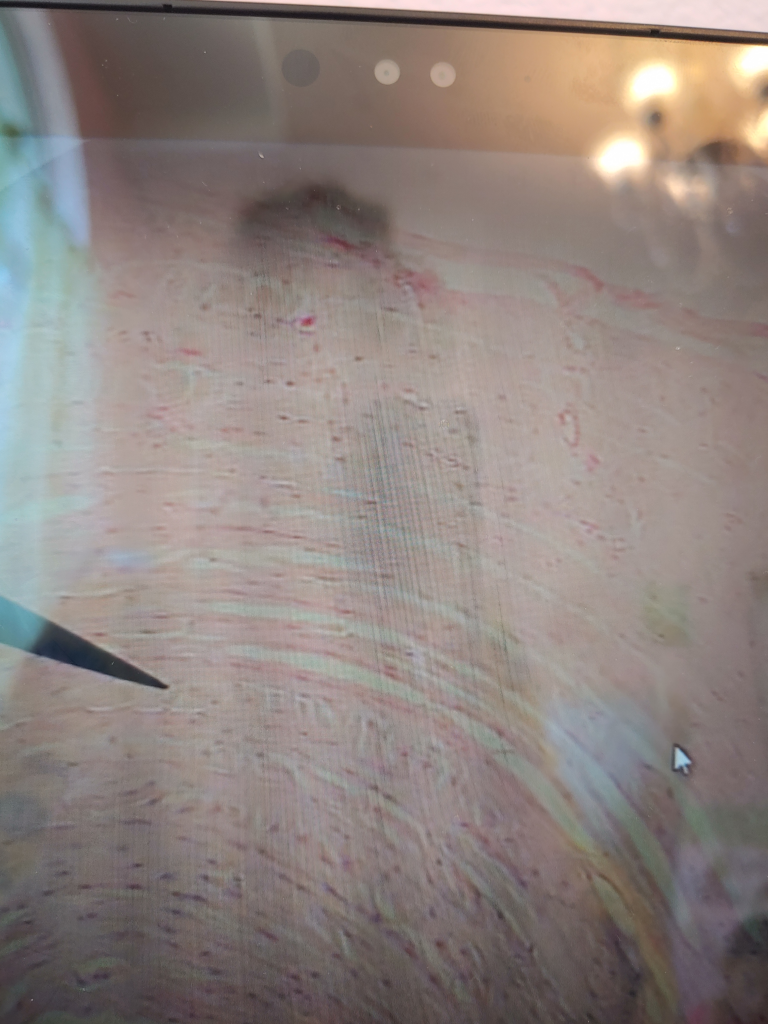
The big whitish open areas of the tissue are called the adipose tissue. This tissue also has fats ( which are the purple dots in the adipose tissue ) which are called the nuclei. Another major feature of the adipose tissue would be the cytoplasmic membrane which is the strands that are connected to the nuclei which form the adipose cells.
FUN FACT: Adipose tissue can comprise cell containing fat and oil.
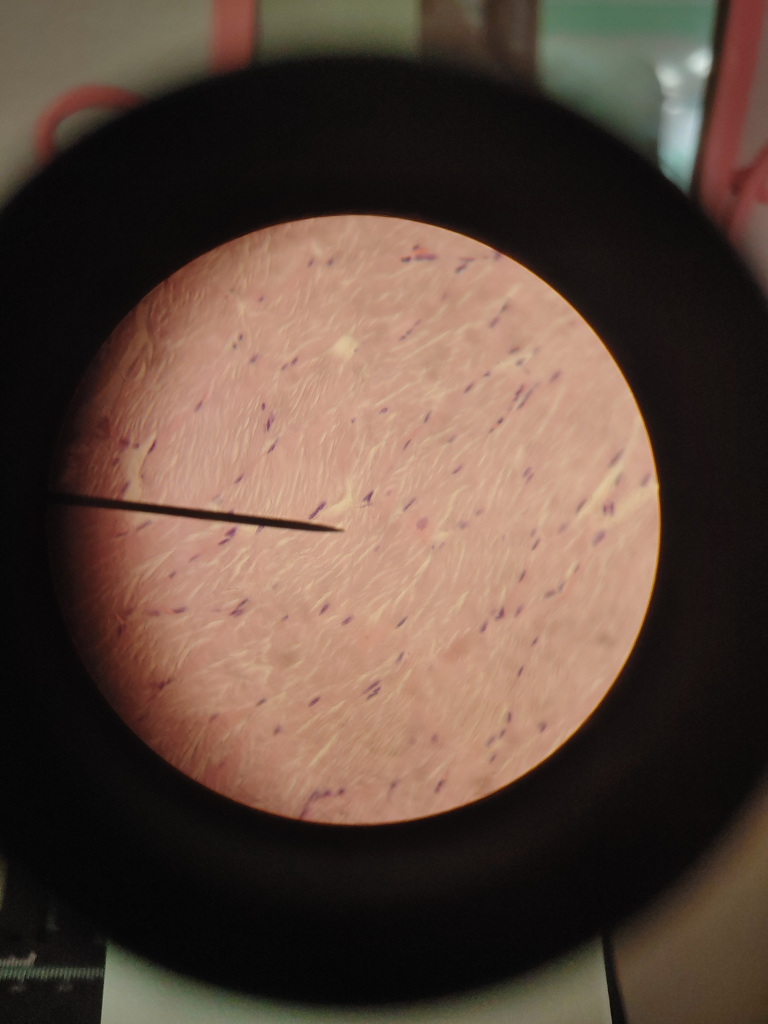
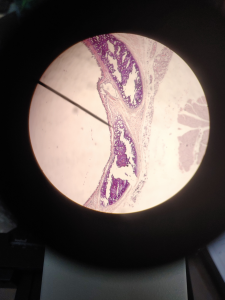
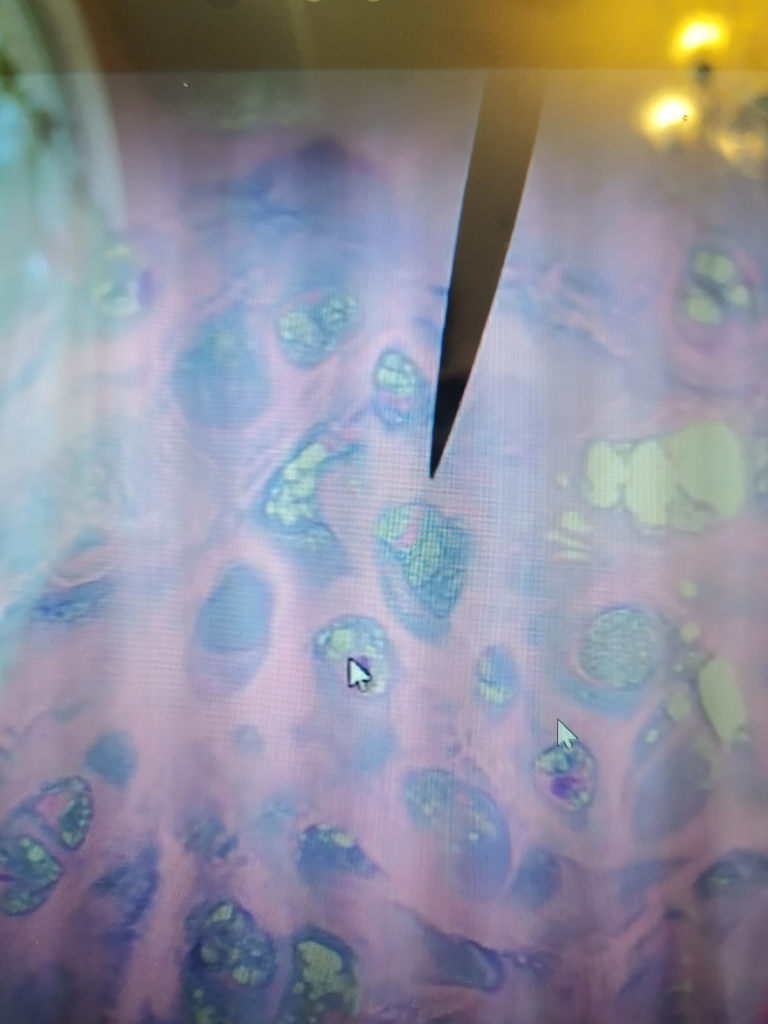
The picture above is a picture of Fibrocartilage through a microscope. The fibers in Fibrocartilage are dense like hairs. The nuclei in Fibrocartilage are in little clusters/lines. The purple dots in the Fibrocartilage is called chondrocytes which is the nuclei in the tissue.
FUN FACT: Fibrocartilage is made up of ground substance and chondrocytes.
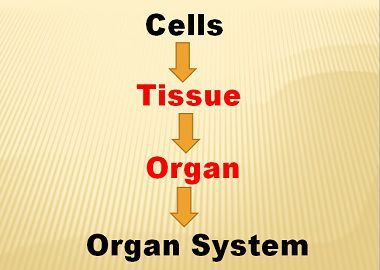
CELLS:
- Are the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism
- Main purpose of a cell is to organize
Examples: Blood cells , Muscle cells , Fat cells , etc.
FUN FACT ABOUT CELLS: Cells are made up of proteins and organelles
TISSUES:
- Capable of performing the simple task
- If there is some damage in the tissue it can be repaired by fibrosis
Examples: Nerve tissue, Muscles tissue, Connective tissue, etc.
FUN FACT ABOUT TISSUES: Fat and muscle are types of tissue
ORGANS:
- Different organs work for different purposes
- Size is greater than a tissue
Examples: stomach, lungs, heart, brain,etc.
BOTH TISSUES AND ORGANS:
- Tissues and Organs are made up of cells
- Both are found in multicellular organisms

FUN FACT: Fibrocartilage is a very strong and tough tissue found at the insertions of ligaments and tendons.
FUNCTION:

FUNCTION: They give elastic cartilage great flexibililty and strength and elasticity to certain parts of the body like ears.
FUN FACT:Elastic Cartilage contains elastic fibers in addition to collagen 🙂
The elastic cartilage contains elastic fiber networks and collagen type II fibers. The principal protein is elastin. Another thing is that elastic cartilage is a type of cartilage present in the outer ear.
FUN FACT: Your right lung is heavier than your left lung
FUNCTION: The lung tissue keeps you alive and healthy
- Inhalation and Exhalation
- External Respiration Exchanges Gases
- Internal Respiration Exchanges Gases
- Air Vibrating the vocal cords creates sound